Handling Errors
Retry single component after error
This example was originally created as one of several examples I wrote for a post about errors and retry for React Server Components. See that post for a more detailed explanation of the concepts here.
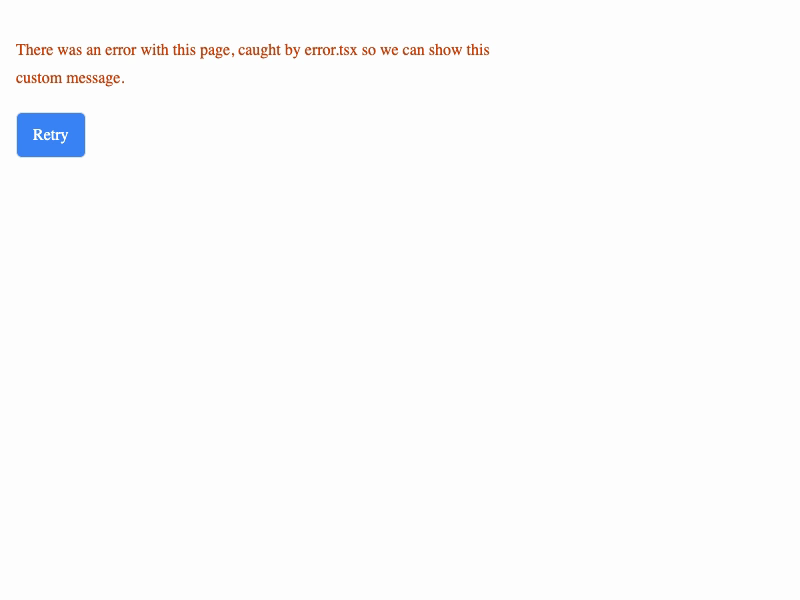
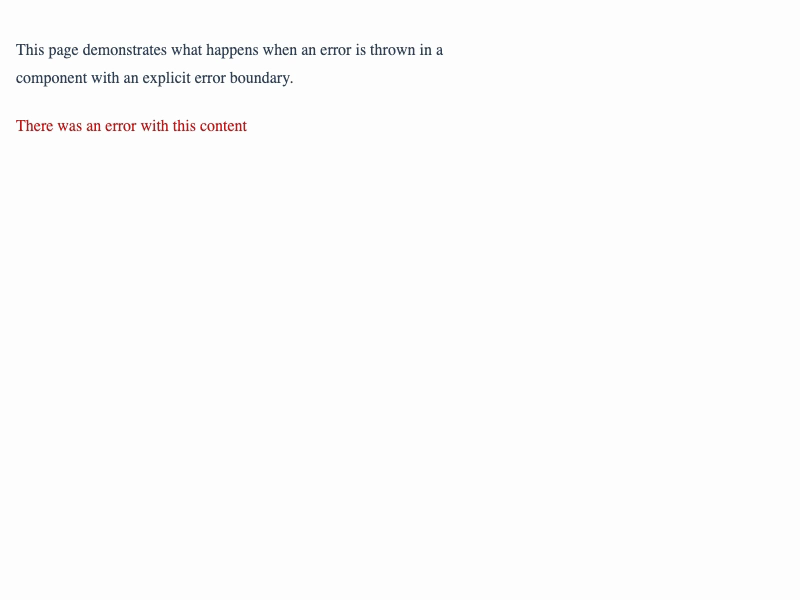
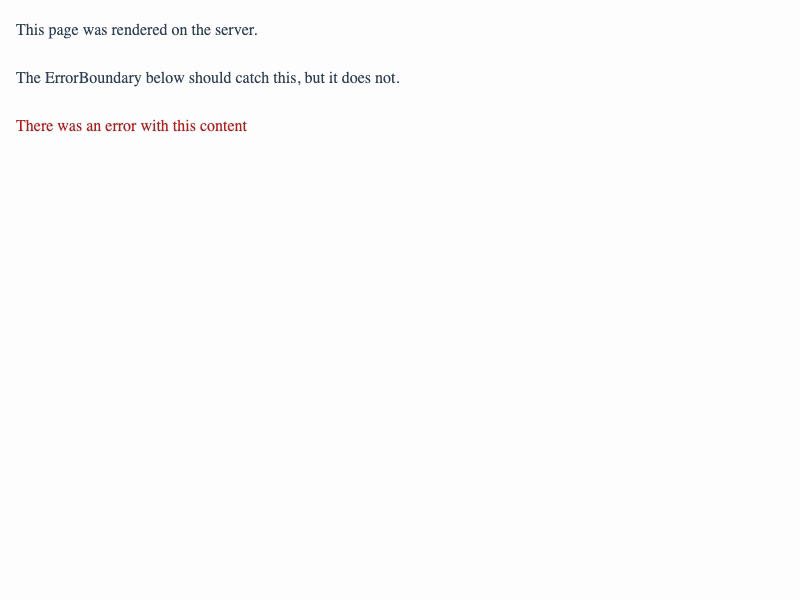
If a component on our page throws an error, we can either catch it at the page level via error.tsx, or we can wrap the error-prone component in an ErrorBoundary so that we can render the rest of the page even if that component fails.
Here's a Page that has a child component that throws an error 50% of the time, wrapped in an ErrorBoundary:
If that error is thrown, our ErrorFallback fallback will be rendered. This fallback includes a Reset button that will reset the page when clicked. That process is handled by the retry function, which calls router.refresh() to reset the page.
While the page is being reset, we show a spinner to indicate that the page is loading. This spinner is a simple component that we've created called Spinner. This complicates the example a little, but is useful UX to show your user that something is happening, especially if the component that errored is a heavy or slow-loading one.
Our ErrorFallback.tsx component receives a resetErrorBoundary function as a prop, which is passed in automatically by next.js. However, calling resetErrorBoundary() will not reset the page. Instead, we need to call router.refresh() to reset the page. We also wrap this in a startTransition to ensure that the page doesn't flicker when we reset it.
The reset() function does not actually reset the component, or the page,
just the state of the error boundary. To retry the render, you need to call
router.refresh().
The call to router.refresh() will cause the entire page to re-render, so it's not as surgical as simply reloading a single component. However, it's a good way to give the user a way to recover from an error without having to refresh the entire page. To the user it will look like the component is being reloaded, which is often good enough.
Because router.refresh() works asynchronously (we're going over the network to re-render on the server, after all), but does not return a Promise, we can't use async/await syntax here. Thankfully, we can wrap that call in a startTransition, which will automatically have React update the UI once the new RSC payload is received.
Live Demo
There's a 50% chance that this example will throw an error. If it does, a Reset button will appear that you can click to reset the page. Otherwise, hit the refresh button above the iframe to try it again.