Handling Errors
Using error.tsx
This example was originally created as one of several examples I wrote for a post about errors and retry for React Server Components. See that post for a more detailed explanation of the concepts here.
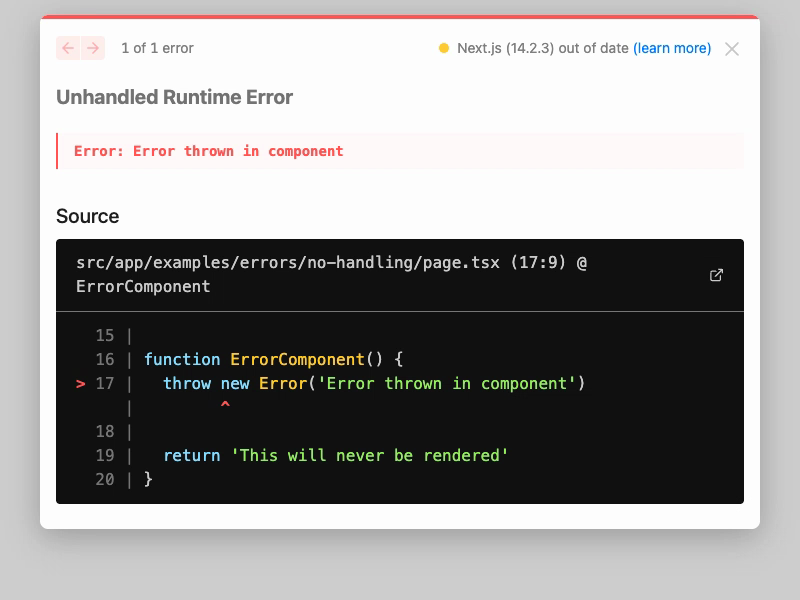
When you render a page that throws an error, you can catch it using the error.tsx convention. This is a file that you can create in the same directory as the page that is throwing the error, and it will be used to render an error message when an error is thrown.
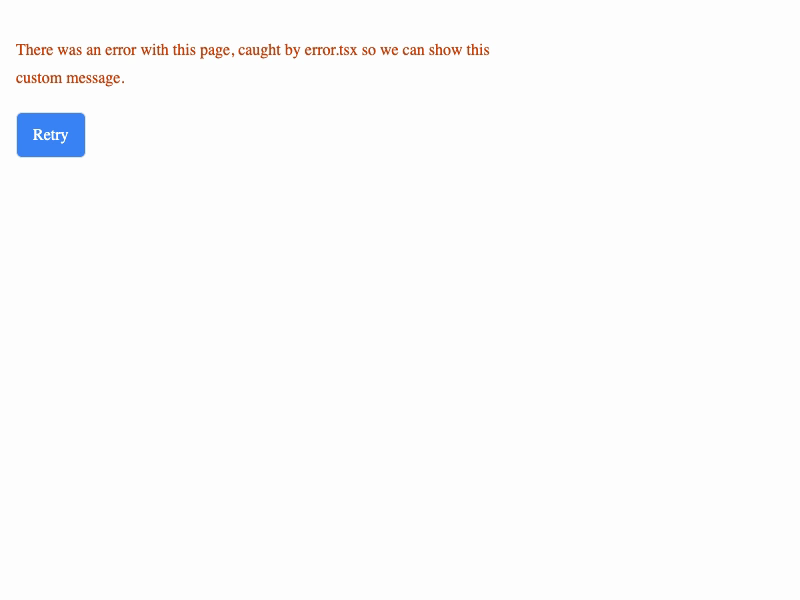
Although we didn't catch the error in ErrorComponent, we can still provide a custom error message by creating an error.tsx file in the same directory as the page that is throwing the error. Here's what that looks like:
error.tsx must be a client component
If you take this approach, the error.tsx file must be a client component. This is because the error is caught on the client side, and the error message is rendered in the client. If you try to use a server component for error.tsx, you'll see an error in the console.
When you run this page, you'll see the error message from error.tsx instead of the error message from the thrown error. This is a great way to provide a better user experience when errors occur in your app than what happens by default, but it's still a bit heavy-handed as the entire app is affected by the error.
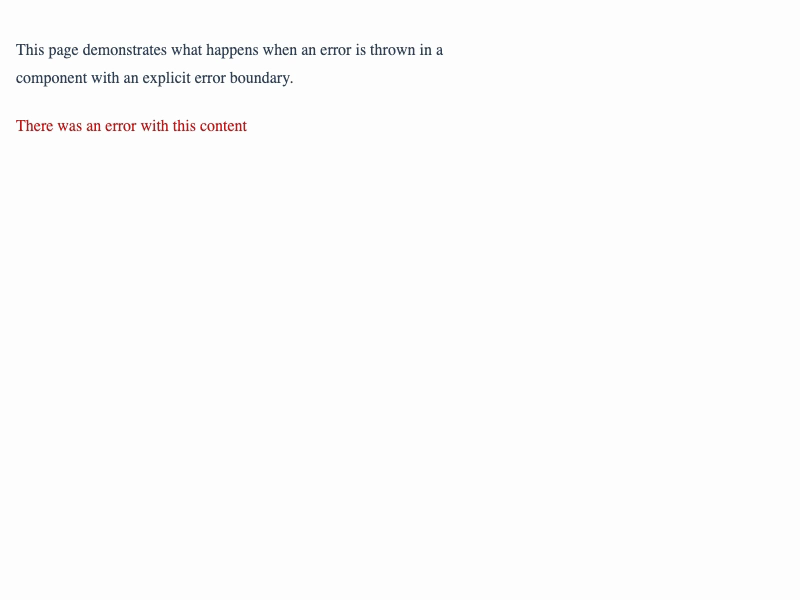
If you can, it's better to be intentional about where you catch errors, so your user can still see all of the other content on the page. This is where explicit error boundaries come in.
Live Demo
This example can't be easily inlined as it demonstrates how a full-page feels to the end user. Here it is inside an iframe, and there's a looping video below too.